16 November 2012
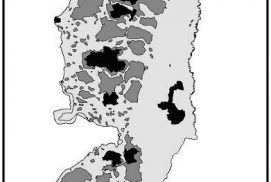
A growing chorus of Israeli, Palestinian and international voices are questioning whether a two-state framework for the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is still applicable given the current realities on the ground in the Occupied Palestinian Territories (OPT). Nineteen years since the signing of the Oslo Accords in September 1993 and notwithstanding a massive international effort towards the creation of an independent Palestinian state, a lasting solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict is still a distant and by no means guaranteed outcome. The two-state framework, based on a partition of the land and the creation of a yet-to-be defined Palestinian state living side by side with Israel is by far the most accepted outcome for the conflict. It is endorsed by the great majority of domestic and international players and according to opinion polls still enjoys a sizable majority among the respective Israeli and Palestinian communities.